ChoiceNet - How It Works
The following steps you through what takes place when a user named Timmy logs into the Internet via Lucent's PortMaster Communications Server. Timmy's login user-id/password will only permit him to go to approved sites.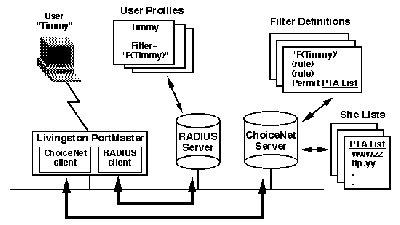
1. Timmy logs into the PortMaster.
2. The PortMaster sends Timmy's login to the RADIUS server to authenticate.
3. The RADIUS server examines Timmy's name and password in Timmy's user profile.
4. When the RADIUS server sends back a verification acknowledgment to the PortMaster, it also includes the name of a filter. In this case, the filter "F(Timmy)"is to be applied to user Timmy.
5. The PortMaster checks to see if the filter, called "F(Timmy)", is stored locally in its memory. If it is, the PortMaster uses it. If not, it sends a request to the ChoiceNet server to download the filter "F(Timmy)" which is maintained in the PortMaster memory for the remainder of Timmy's session.
6. Timmy initiates a web connection to www.playboy.com.
7. The PortMaster looks at each filter rule found in "F(Timmy)", starting from the top. When it reaches the rule permit "PTA List", the PortMaster looks into its local cache to see if www.playboy.com is on the PTA List. If not, the PortMaster sends a filter look-up request to the ChoiceNet server. This look-up contains the list name "PTA List" and the site Timmy is trying to access (www.playboy.com).
8. The ChoiceNet server searches the list and sends back the result.
9. Based on the result, the PortMaster either permits or denies access and updates its local cache. In the event of denial of service, the PortMaster sends a denial notification message back to Timmy informing him that he can't access that site.